General
BME P58 •0•0 processors can execute single-task and multi-task applications. Unlike a single-task application, which only executes master tasks, a multi-task application.defines the task execution priorities.
Master Task
The master task represents the application program’s main task. You can choose from the following MAST task execution modes:
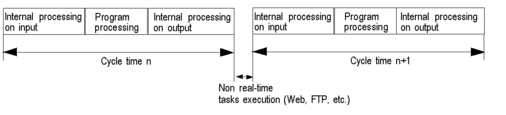
Cyclical (default setup): Execution cycles are performed in sequence, one after the other.
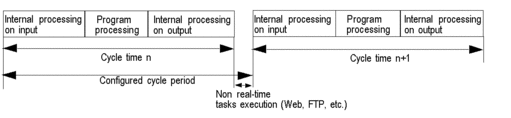
Periodical: A new cycle is started periodically, according to a user-defined time period (1 - 255 ms).
If the execution time is longer than the period configured by the user, the bit
%S19is set to 1, and a new cycle is launched.
The following illustration shows the cyclical execution of the MAST task:
The following illustration shows the periodical execution of the MAST task:
Both MAST task cycle modes are controlled by a watchdog.
The watchdog is triggered if the MAST task execution time is longer
than the maximum period defined in the configuration, and causes a
software error. The application then goes into HALT status, and the
bit %S11 is set to 1 (the user must reset it to 0).
The watchdog value (%SW11) may be configured
between 10 ms and 1,500 ms (default value: 250 ms).
In periodical operating mode, an additional check detects when a period has been exceeded. The PLC will not switch off if the period overrun remains less than the watchdog value.
Bit %S19 signals a period overrun. It is set
to 1 by the system when the cycle time becomes longer than the task
period. Cyclical execution then replaces periodical execution.
The MAST task can be checked with the following system bits and system words:
System Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
MAST task period |
|
Activation of the master task |
|
Watchdog default |
|
Period exceeded |
|
Last cycle overhead time (in ms) |
|
Longest overhead time (in ms) |
|
Shortest overhead time (in ms) |
|
Last cycle execution time (in ms) |
|
Longest cycle execution time (in ms) |
|
Shortest cycle execution time (in ms) |
Fast Task
The FAST task is for periodical processing and processing over short durations.
FAST task execution is periodical and must be quick so that no lower priority tasks overrun. The FAST task period can be configured (1 - 255 ms). The FAST task execution principle is the same as for periodical execution of the master task.
The FAST task can be checked with the following system bits and system words:
System Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
FAST task period |
|
Activation of the fast task |
|
Watchdog default |
|
Period exceeded |
|
Last cycle execution time (in ms) |
|
Longest cycle execution time (in ms) |
|
Shortest cycle execution time (in ms) |
Event Tasks
With event processing, the application program’s reaction time can be reduced for events originating from:
input/output modules (EVTi blocks)
events timers (TIMERi blocks)
Event processing execution is asynchronous. The occurrence of an event reroutes the application program towards the process associated with the input/output channel, or to the event timer that caused the event.
Event tasks can be checked with the following system bits and system words:
System Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Activation of events processing |
|
Saturation of the event signal management stack. |
|
Number of IO events and telegram processes executed NOTE: TELEGRAM is available only
for PREMIUM (not on Quantum neither M340)
|
Single Task Execution
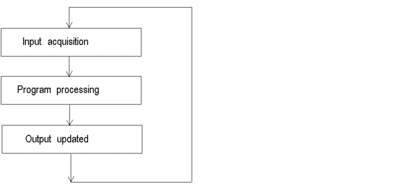
A single-task application program is associated with one task; the MAST task.
The following diagram shows a single-task application’s execution cycle:
Multi-Task Execution
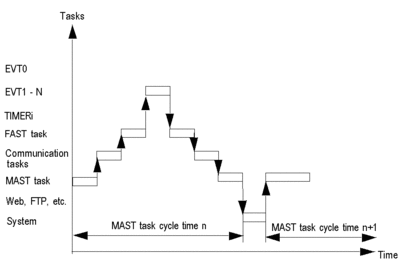
The following diagram shows the level of priority of the tasks in a multi-task structure:

The following diagram shows the execution of tasks in a multi-task structure: