Scope of the grounding system
The grounding system for an electrical system creates the connection to earth and must meet the following requirements:
Discharge the voltage from touchable metallic system parts (chassis) to protect people from electric shocks
Discharge over-currents from direct lightning strikes to earth
Discharge induced currents from atmospheric discharges between two points of a power transmission line to earth
EMC performance and guidelines for the grounding system
System |
EMC performance |
Guidelines for use |
|---|---|---|
TT |
Conditionally suitable Between the ground connection of the primary distribution network and the leakage current from the electrical system, that are caused by ground faults within the system. As with transient currents, potential difference occurs due to the leakage current from devices. These transient currents can lead to faulty couplings or even faults within the system. A corrective measure here is a equipotential bonding conductor between the devices connected directly to earth. These measures basically convert the TT system into a TN-S system. |
|
TN-C TN-C-S |
Bad Because the functions and protective earth conductor are combined in TN-C and TN-C-S systems, current feedback occurs on the PEN conductors during normal operation. Current feedback from devices via the PEN conductors can lead to faulty couplings. |
|
TN-S |
Very good The TN-S system is the best solution from an EMC point of view. The PE conductors have no power in normal operation. |
|
IT |
Bad Note: The IT system is recommended as intrinsically safe for safety matters since no electric arcs can occur. |
|
Recommended grounding system connection scheme
The following illustration shows a typical connection scheme for a grounding system:
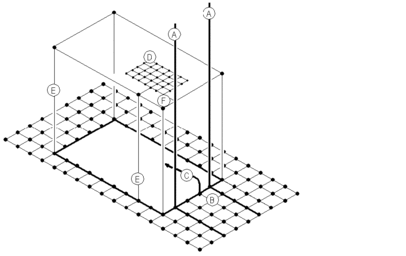
A Lightning arrester down-lead
B Underground meshed earthing system with reinforcement at foot of the down-lead
C System ground connection, connected to the equipotential bonding strip, to which the PE conductor or PEN conductor are connected in turn
D Earthing system for a system section with integral metallic structures or additional ground connections (E)
E Interconnection between the lightning arrester down-lead and the earthing system as well as other metal structures in the vicinity


