Differential mode interference
A differential mode interference is caused if an interfering voltage is coupled into one branch of a circuit only. A potential difference is then caused between the outgoing and return wires. Causes are currents in the outward and return conductors to the earth reference plane in opposite directions. The interfering circuit closes exclusively with a galvanic connection.
Circuit diagrams for a symmetrically and an asymmetrically operated electrical circuit with differential mode interference.
Differential mode interference in a symmetrically operated electrical circuit 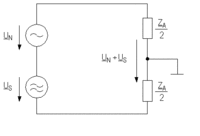 |
Differential mode interference in an asymmetrically operated electrical circuit 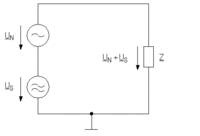 |
Character definitions
Character |
Meaning |
|---|---|
UN |
Wanted Voltage |
US |
Interference voltage |
Z |
Impedance (e.g. in measurement device) |
Causes
Common mode interferences have many different causes and are coupled either inductive or capacitive:
Switching frequency and the respective harmonic waves
Oscillations that can be caused by capacitance or inductance of components or wiring arrangements (parasitic)
Common mode-differential mode-conversions in unwanted asymmetries on the circuit


