The time service synchronizes computer clocks over the Internet. For example, the time of one client is synchronized either with another server or to a referenced time source like a radio or satellite receiver.
Typical time service configurations utilize multiple redundant servers and diverse network paths to achieve high accuracy and reliability. Time service accuracy can be within a millisecond on LANs and up to a few tenths of milliseconds on WANs.
Use the time service for:
-
event recording: sequence events
-
event synchronization: trigger simultaneous events
-
alarm and I/O synchronization: time stamp alarms
Time Synchronization and Time Stamps
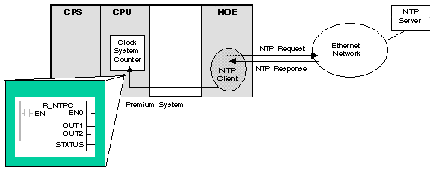
On an Ethernet network, all controllers should be synchronized with the same clock time, which is provided by an server. In each application program, events or application data (I/O values for example) can be time stamped using the application stacks.
The Ethernet interface module connects to an NTP time server and provides the source-time synchronization signal, which is sent to the CPU.
To read the clock, a function block is used in the controllerís project (application program):