|
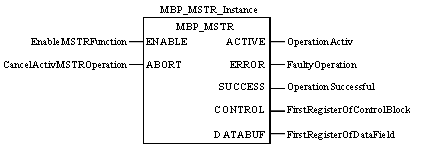
Using the MBP_MSTR Block for Mail Service Communication
|
|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Parameter
|
Data Type
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
ENABLE
|
None
|
ON = enables selected MBP_MSTR operation
|
|
|
ABORT
|
None
|
ON = terminates active MBP_MSTR operation
|
|
|
ACTIVE
|
None
|
ON while the instruction is active
|
|
|
ERROR
|
None
|
ON if the MBP_MSTR operation is terminated prior to completion
|
|
|
SUCCESS
|
None
|
ON = operation successful
|
|
|
CONTROL
|
INT, UINT
|
Control block is the first of several network-dependant, contiguous, holding words, and the first of nine contiguous words entered in the top node.
The remaining eight words are:
|
|
|
Displayed: Identifies one of the MBP_MSTR = 13
|
|||
|
First implied
|
displays error status (see Mail Service Error Codes)
|
||
|
Second implied
|
displays length (number of words transferred)
|
||
|
Third implied
|
(not used)
|
||
|
Fourth implied
|
high byte: slot address of the NOE module or 0xFE for the 140 CPU 651 x0
|
||
|
low byte: 0 (not used)
|
|||
|
Fifth implied
|
(not used)
|
||
|
Sixth implied
|
(not used)
|
||
|
Seventh implied
|
(not used)
|
||
|
Eighth implied
|
(not used)
|
||
|
DATABUF
|
INT, UINT
|
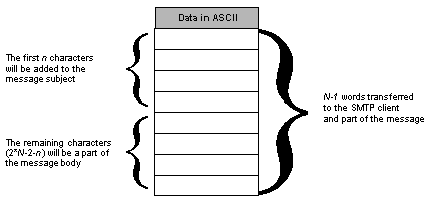
The DATABUF parameter is the address of the buffer including the data inserted into the body of the email message. The data should be in ASCII format starting at the second word.
Note:
|
|
|
Byte Number
|
Description
|
Value
|
|---|---|---|
|
1 (least significant byte)
|
Mail header
|
{1, 2, 3}
|
|
2 (most significant byte)
|
Nb n of extra characters in subject
|
User-defined (between 0 and 238)
|