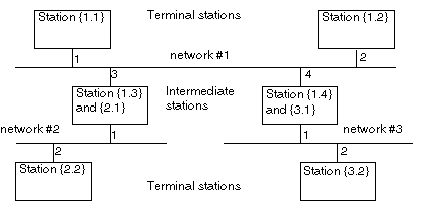
An X-Way PLC architecture is comprised of various network levels that interconnect via intermediate stations.
In a multi-network architecture, a single logic link must exist between two terminal stations.
Example
A terminal station is addressed by the {network address . station address} pairing.
Terminal stations receive the messages intended for their network address, as well as the general broadcast messages, and send to their network connection all the messages intended for a remote station.
An intermediate station has as many network addresses as it has connection points to different networks. One of its addresses is considered to be the main address and has the role of guaranteeing access to all the communication entities of a routing station.
Intermediate stations are classified in two categories:
-
Multicoupler stations
-
Bridge stations
These provide management of various network couplers and guarantee all the mono-network services on the various network segments (common words, telegrams, messaging). They do not offer routing between the various network connections.
These provide the same functions as the multi-coupler stations and also guarantee transparency of communication between the various network connections.