Description
The following program is a short demo application with four instances of XXMIT showing the four main functions:
Modbus Master
Simple ASCII In
ASCII Message Out
Terminated ASCII In
Modbus Master
The following Modbus Master operation is a read request to a slave (address 4 for example) device connected to port 1 of the master:
Read slave's %MW1 to %MW10
into local %MW11 to %MW20
The Slave (address 4) must be set up with the following port parameters:
9600 baud
8 data bits
1 stop bit
even parity (2)
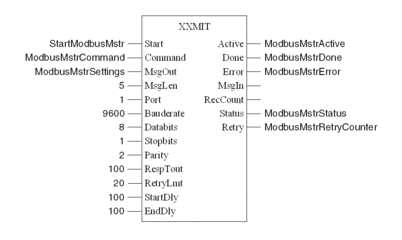
The Master uses settings from XXMIT
Variable declaration for Modbus Master
The following table shows the variables used in the Modbus Master example:
Variable Name |
Data Type |
Initial Value |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
StartModbusMstr |
BOOL |
||
ModbusMstrActive |
BOOL |
||
ModbusMstrCommand |
WORD |
16#0100 |
Bit 8 set |
ModbusMstrDone |
BOOL |
||
ModbusMstrError |
BOOL |
||
ModbusMstrSettings |
WordArr9 |
||
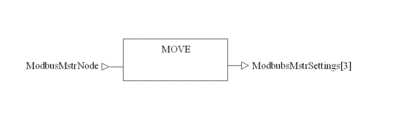
ModbusMstrSettings[1] |
3 |
Modbus Code: Read multiple words |
|
ModbusMstrSettings[2] |
10 |
Amount of Words to read |
|
ModbusMstrSettings[3] |
4 |
Slave Modbus address |
|
ModbusMstrSettings[4] |
1 |
Source word |
|
ModbusMstrSettings[5] |
11 |
Destination Word |
|
ModbusMstrSettings[6] |
0 |
not used |
|
ModbusMstrSettings[7] |
not used |
||
ModbusMstrSettings[8] |
not used |
||
ModbusMstrSettings[9] |
not used |
||
ModbusMstrStatus |
INT |
||
ModbusMstrNode |
WORD |
4 |
Enter Slave address |
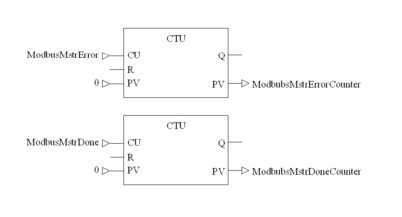
ModbusMstrErrorCounter |
INT |
||
ModbusMstrDoneCounter |
INT |
IEC Section for Modbus Master
Program the following in an FBD section:
Slave node address assignment
Assignments to the XXMIT function block:
Count errors and successes
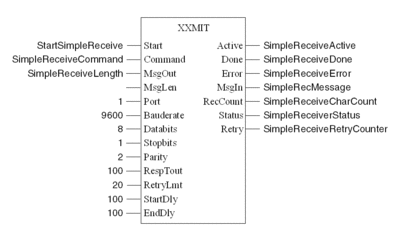
Simple ASCII Receive
Receives whatever comes into port 1. The receive buffer's length is assigned as 'SimpleReceiveLength', which has an initial value of 10.
Received characters are in MsgIn array, number of received characters in RecCount.
Variable declaration for Simple ASCII Receive
The following table shows the variables used in the Simple ASCII Receive example:
Variable Name |
Data Type |
Initial Value |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
StartSimpleReceive |
BOOL |
||
SimpleReceiveActive |
BOOL |
||
SimpleReceiveCharCounter |
INT |
||
SimpleReceiveCommand |
WORD |
16#0480 |
Bits 7 and 10 set. FIFO enabled |
SimpleReceiveDone |
BOOL |
||
SimpleReceiveError |
BOOL |
||
SimpleReceiveLength |
INT |
10 |
|
SimpleReceiveRetryCounter |
INT |
||
SimpleReceiveStatus |
INT |
||
SimpleRecMessage |
ByteArr12 |
||
SimpleReceiveDoneCounter |
INT |
||
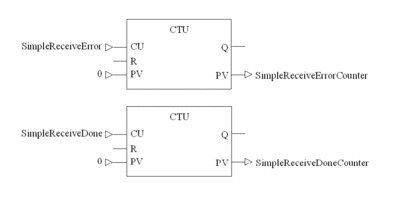
SimpleReceiveErrorCounter |
INT |
IEC Section for Simple ASCII Receive
Program the following in an FBD section:
Count errors and successes
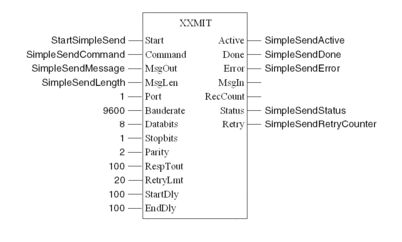
Simple ASCII Send
Sends a simple ASCII message out off port 1, the message is 'Hello World!!'
Variable declaration for Simple ASCII Send
The following table shows the variables used in the Simple ASCII Send example:
Variable Name |
Data Type |
Initial Value |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
StartSimpleSend |
BOOL |
||
SimpleSendActive |
BOOL |
||
SimpleSendCommand |
WORD |
16#0200 |
Bit 9 set |
SimpleSendDone |
BOOL |
||
SimpleSendError |
BOOL |
||
SimpleSendLength |
INT |
14 |
Number of characters to send |
SimpleSendMessage SimpleSendMessage[1] SimpleSendMessage[2] SimpleSendMessage[3] SimpleSendMessage[4] SimpleSendMessage[5] SimpleSendMessage[6] SimpleSendMessage[7] SimpleSendMessage[8] SimpleSendMessage[9] SimpleSendMessage[10] SimpleSendMessage[11] SimpleSendMessage[12] SimpleSendMessage[13] SimpleSendMessage[14] |
ByteArr36 |
16#48 16#65 16#6C 16#6C 16#6F 16#20 16#57 16#6F 16#72 16#6C 16#64 16#20 16#21 16#21 |
'Hello World !!' |
SimpleSendRetryCounter |
INT |
||
SimpleSendStatus |
INT |
||
SimpleSendDoneCounter |
INT |
||
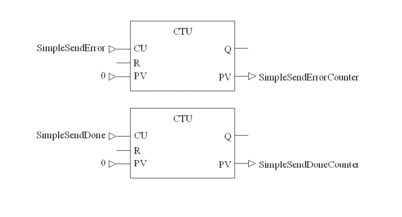
SimpleSendErrorCounter |
INT |
IEC Section for Simple ASCII Send
Program the following in an FBD section:
Count errors and successes
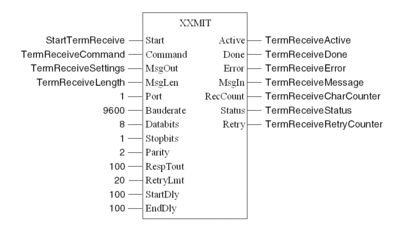
Terminated ASCII Receive
After receiving the 'starting characters' "AB", the function block puts all received characters into the receive buffer MsgIn. The receiver will stop when the 'finishing characters' "CD" are received, whereby the "Done" output will be set, to indicate the successfull completion. The max. length of the receive buffer is assigned as "TermReceiveLength", which is set to an initial value of 20 in this example.
Variable declaration for Terminated ASCII Receive
The following table shows the variables used in the Terminated ASCII Receive example:
Variable Name |
Data Type |
Initial Value |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
StartTermReceive |
BOOL |
||
TermReceiveActive |
BOOL |
||
TermReceiveCharCounter |
INT |
||
TermReceiveCommand |
WORD |
16#0880 |
Bits 11 and 7 set. FIFO enabled |
TermReceiveDone |
BOOL |
||
TermReceiveError |
BOOL |
||
TermReceiveLength |
INT |
20 |
|
TermReceiveMessage |
ByteArr36 |
Received characters |
|
TermReceiveRetryCounter |
INT |
||
TermReceiveSettings TermReceiveSettings[1] TermReceiveSettings[2] TermReceiveSettings[3] TermReceiveSettings[4] TermReceiveSettings[5] TermReceiveSettings[6] |
ByteArr36 |
16#02 16#02 16#41 16#42 16#43 16#44 |
length of termination string (1 or 2) length of start string (0, 1 or 2) 1st start character 2nd start character 1st termination character 2nd termination character |
TermReceiveStatus |
INT |
||
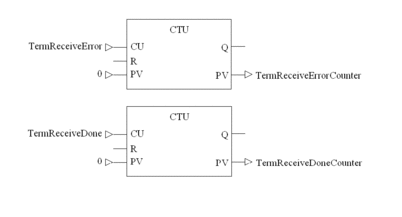
TermReceiveDoneCounter |
INT |
||
TermReceiveErrorCounter |
INT |
IEC Section for Terminated ASCII Receive
Program the following in an FBD section:
Count errors and successes
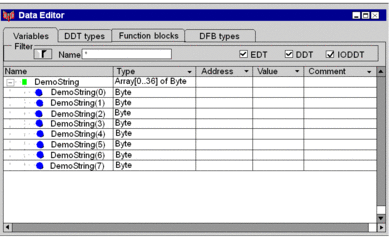
Entering Strings as initial values
The Data Editor of Control Expert allows you to easily enter Strings as initial values into byte arrays.
The following part gives a short describtion of how to define a variable 'DemoString' as 'ByteArr36' and enter a string 'My Text ! ' as initial value.
Open the Data Editor
From the main menu select:
Tools -> Data Editor.Data Editor
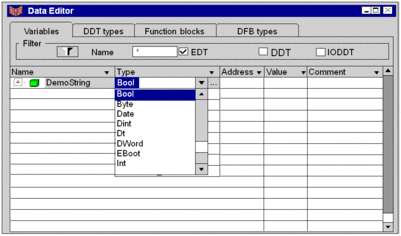
Declaring new String name
Declare stringname
for Array by clicking on  next to type (in this case
bool) This will then open a variable type selection window.
next to type (in this case
bool) This will then open a variable type selection window.
Define Element Type 1
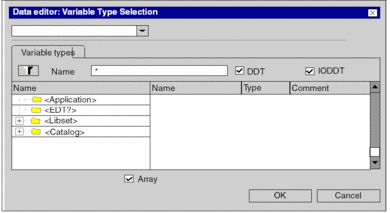
Define Element Type
Check the Array checkbox and define array element type and number of elements. It is now possible to see and modify values for expanded byteArr36.
Define Element Type 2
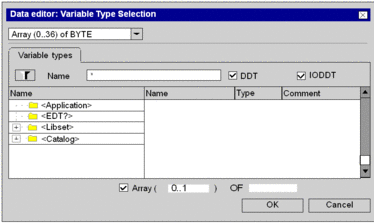
Definition ByteArr36