At a Glance
Let us
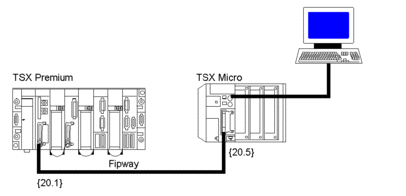
assume we want to send a character string Str_1 from
station 1 of network 20 to the terminal port of station 5, then receive
a character string Str_2 from the terminal port of
station 5 of the same network.
Here, a video terminal is connected to the terminal port of station 5 of network 20.
The string to be sent contains 10 characters.
The function's management
table is made up of the table of words %MW170:4.
Illustration
The two stations are connected via a Fipway network.
Programming
Programming in ST:
IF RE(%I0.3.8) AND NOT %MW170.0 THEN (* initialization of the data to send *) %MW173 := 10; (* communication function *) OUT_IN_CHAR(ADDR(’{20.5}0.0.0.SYS’),1,Str_1,%MW170:4,Str_2);END_IF;Request parameters:
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
ADDR(‘{20.5}0.0.0.SYS’) |
|
1 |
Transmission then reception |
Str_1 |
Variable of type |
%MW170:4 |
Management table |
Str_2 |
Variable of type |
At the end of the exchange, %MW173 will contain the length of the data received (in bytes).


