At a Glance
On Modicon
M340 PLCs, forced bits are not accessed by READ_VAR and WRITE_VAR functions as Modbus protocol does
not support it. Therefore the following statements about forced bits
cannot be applied to Modicon M340 PLCs.
The following examples
illustrate the READ_VAR communication function for
reading bits. In this case the receive table consecutively contains
the value of the bits as well as the forcing indication.
Reading 32 internal bits
In ST, the syntax of the internal bit reading function is as follows:
READ_VAR (ADDR(‘{20.1}0.5.1.3’),‘%M’,
0, 32, %MW100:4, %MW50:4);
The receive table must include 8 bytes (4 words), 4 bytes for the value and 4 bytes for the forcing indication.
Word |
Byte 3 |
Byte 2 |
Byte 1 |
Byte 0 |
|
Value |
%MW100 |
0000 |
0000 |
1100 |
1100 |
%MW101 |
1111 |
1111 |
0000 |
1111 |
|
Forcing |
%MW102 |
0000 |
0000 |
0101 |
0101 |
%MW103 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
1111 |
Forcing can be performed for each %MW102 or %MW103 bit set to 1; the forcing value being
that of the corresponding bit read.
Example:
Value of the first 4 bits (byte 0 of word %MW100) |
Forcing of the first 4 bits (byte 0 of word %MW102) |
Description |
0 |
1 |
The bit is forced to 0 |
0 |
0 |
The bit is not forced |
1 |
1 |
The bit is forced to 1 |
1 |
0 |
The bit is not forced |
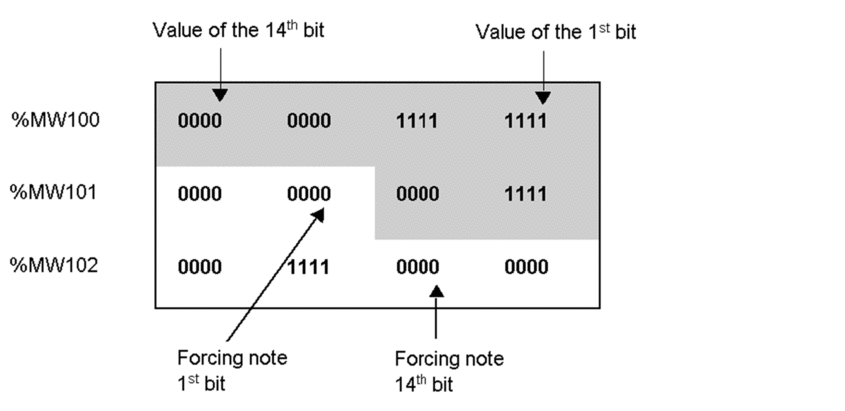
Reading 18 internal bits
In ST, the syntax of the internal bit reading function is as follows:
READ_VAR (ADDR(‘{20.1}0.5.1.3’),‘%M’,
0, 18, %MW100:3, %MW50:4);
The receive table must contain 3 words (or 6 bytes). In fact, to obtain the value of the 18 bits, 3 bytes plus a further 3 bytes are needed in order to contain the forcing value of the 18 bits.