|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
%
|
I or Q
|
X, W or D
|
r
|
•
|
m
|
•
|
c
|
•
|
d
|
.
|
j
|
|
Symbol
|
Type of object
I = input
Q = output
|
Format
X = boolean
W = word
D = double word
|
Rack address
r = 0 to 7
|
Position of module
m = 00 to 14
|
Channel No.
c = 0
|
Rank
d = 0 to 253
|
Bit j
j = 0 to 15
|
||||
|
Inputs/Outputs
|
Physical addressing
|
Logical addressing
|
|---|---|---|
|
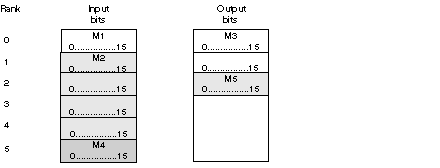
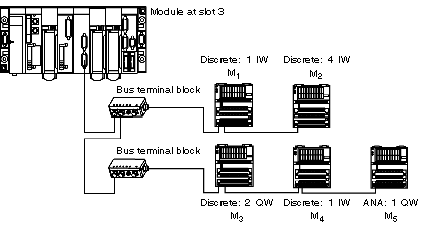
M1: access to input 7
|
%IW0.3.0.0..6
|
%IW0.3.0.0.6
|
|
M2: access to input 24
|
%IW0.3.0.2.7
|
%IW0.3.0.7.7
|
|
M3: access to output 3
|
%QW0.3.0.0.2
|
%QW0.3.0.0.2
|
|
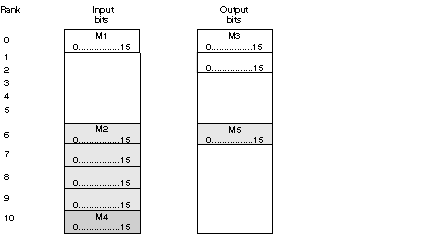
M4: access to input 4
|
%IW0.3.0.5.3
|
%IW0.3.0.10.3
|
|
M5: access to the analog output
|
%QW0.3.0.2
|
%QW0.3.0.6
|