|
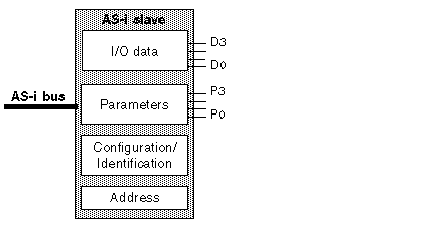
Master profile and structure of a slave
|
|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Element
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
I/O data
|
The outputs are designed for automation components and are transmitted by the master AS-i to the AS-i slave. The input values are stored by the AS‐i slave and made available to the master.
|
|
Parameters
|
AS-i slave parameter states enable the AS-i master to transmit the values that will not be interpreted as input/output data. These parameters can be used for controlling and switching internal operating modes of sensors or actuators.
Examples: motor-starter: slow or fast rotation speed, run, stop, etc. proximity detectors: range, background suppression, etc.
These parameters may be used to correct a calibration dimension during the different operating phases. This function can be performed on slaves with a built-in AS-i connection on the condition that they support this function. Only a master with profile M1 or M2 can modify these parameters.
|
|
Configuration/Identification
|
The input/output configuration (or I/O code) defines the AS-i slave data used as inputs, outputs, or as bi-directional outputs. The I/O configuration (4 bits) is defined by the manufacturer of the slave and is specified in the slave's documentation.
The type of an AS-i slave (or Identification Code) is defined by the I/O configuration but also by an identification code. The latter is coded by each slave on 4 bits. It is also manufacturer-specific and mentioned in the documentation.
|
|
Address
|
At the time of delivery, the address for slaves is 0. So that data may be exchanged, the slaves must be programmed with an address between 1 and 31. The address 0 is reserved for specific functions.
|