In an open environment, after a network identifier has been obtained from the accredited body, the local system administrator is able to manage several subnets.
This will allow local networks to be installed without changing anything for the outside world which will still only be able to see the network indicated by the network identifier.
This sub addressing function is possible by splitting the machine identifier into the following:
-
a subnet identifier
-
a machine identifier
Example: sub addressing for a class B address (IP address in question: 140.186.90.3)
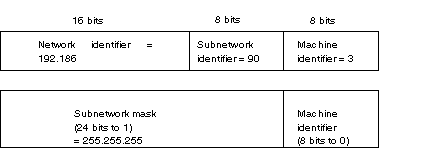
The subnet mask is used to find out the number of bits allocated respectively to the network identifier and the subnet indicator (bits to 1), and then to the machine identifier (bits to 0).
The value of the subnet mask must be chosen to comply with the IP address class. It will have the value (xxx: value chosen left up to the user):
-
for a class A address: 255.xxx.xxx.xxx
-
for a class B address: 255.255.xxx.xxx
-
for a class C address: 255.255.255.xxx
Example: class C subnet mask (IP address in question :192.186.90.3)
NOTE: This division allows 254 possible subnets with 254 machines per subnet.