|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Transmission Rate
|
Lmax
|
ΣLmax
|
TAP Distance
|
ΣLGmax
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 Mbit/s
|
0.3 m (0.98 ft)
|
0.6 m (0.98 ft)
|
1.5 m (4.92 ft)
|
|
|
800 kbit/s
|
3 m (9.84 ft)
|
6 m (19.68 ft)
|
3.6 m (11.81 ft)
|
15 m (49.21 ft)
|
|
500 kbit/s
|
5 m (16.4 ft)
|
10 m (32.8 ft)
|
6 m (19.68 ft)
|
30 m (98.42 ft)
|
|
250 kbit/s
|
5 m (16.4 ft)
|
10 m (32.8 ft)
|
6 m (19.68 ft)
|
60 m (196.84 ft)
|
|
125 kbit/s
|
5 m (16.4 ft)
|
10 m (32.8 ft)
|
6 m (19.68 ft)
|
120 m (393.69 ft)
|
|
50 kbit/s
|
60 m (196.84 ft)
|
120 m (393.69 ft)
|
72 m (236.21 ft)
|
300 m (984.24 ft)
|
|
20 kbit/s
|
150 m (492.12 ft)
|
300 m (984.24 ft)
|
180 m (590.54 ft)
|
750 m (2460.62 ft)
|
|
10 kbit/s
|
300 m (984.24 ft)
|
600 m (1968.49 ft)
|
360 m (1181.09 ft)
|
1500 m (4921.24 ft)
|
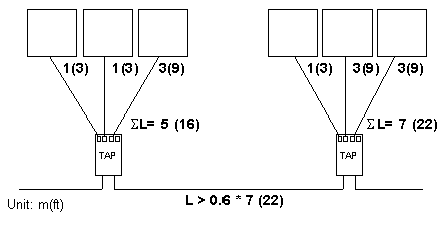
|
Step
|
Description
|
Result
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Calculating the sum of lengths of drop cables for each tap junction.
|
5 m (16 ft) and 7 m (22 ft)
|
|
2
|
Keeping the longest length.
|
7 m (22 ft)
|
|
3
|
Calculating the minimum cable length between the 2 TAPs.
|
60% of 7 m (22 ft)
|