The minimum frequency of the input signal is N (pulses per second) - 5%. Where N is the value set for the parameter Scaling Factor.
The minimum frequency meter value is 950 pulses per 1000 seconds. As a result, the module holds the frequency value to 0 while not receiving N pulses during 1.1 second.
The maximum frequency of the input signal is 500 kHz. That corresponds to a maximum frequency meter value = 500,000,000 pulses per 1000 seconds.
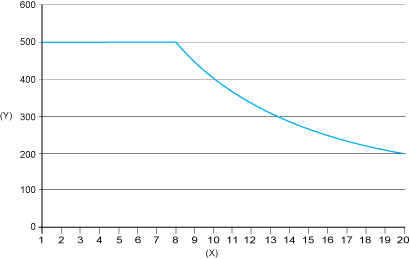
The maximum frequency of the input signal depends on the Sampling Factor. It decreases to 200 kHz for sampling rate = 200 ms.
The following graphic represents the maximum frequency versus Sampling Factor (with Scaling Factor = 1):
X
Sampling factor
Y
Maximum frequency (in kHz)
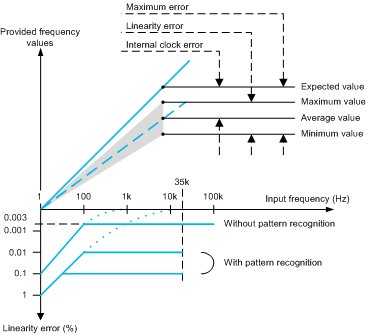
The figure below shows what is the module provided along the frequency range:
For each input frequency, the module provides frequency values close to the expected value (theoretical value).
Accuracy is defined with the relative error between the expected value and the group of provided values (maximum value, minimum value).
The linearity error is the gap between the maximum provided value and the minimum provided value. In usual turbomachinery speed, the linearity error is less than 0.003%.
The internal clock error (+/- 0.01%) is the absolute error due to the internal system clock (Quartz).
To estimate the maximum error of the module, you have to consider the internal clock error in addition to the linearity error.
The pattern recognition system introduces deterioration in accuracy of 0.1% with regular pattern resolution of 1:1000.
The pattern recognition system introduces deterioration in accuracy of 0.01% with fine pattern resolution of 1:10000.
The module round-down the frequency value to 10 mHz instead of 1 mHz when the pattern recognition is operating.