Acquisition of inputs and updates of slave device outputs connected to the AS-i bus are carried out automatically. This occurs at the start and end of each cycle respectively of the task in which the TSX SAY 1000 module is configured.
The user program has access to these inputs and outputs via the language objects.
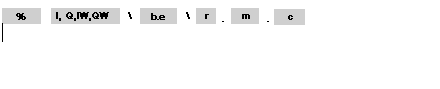
Addressing is defined in the following way:
The table below describes the different elements that make up addressing.
|
Family
|
Item
|
Values
|
Indicates
|
|
Symbol
|
%
|
-
|
-
|
|
Object type
|
I
Q
IW
QW
|
-
-
|
Picture of the All or Nothing input of the module,
Picture of the All or Nothing output of the module,
Picture of the analog input of the module,
Picture of the analog output of the module,
This information is exchanged automatically each cycle of the task to which they are attached.
|
|
Bus and slave No.
|
b
|
2 to 999
|
Bus number.
Except the value 2 if Fipio is used.
|
|
e
|
1 to 31
101 to 131
|
Slave number for bank A.
Slave number for bank B (offset of 100 in relation to the slave number of bank A).
|
|
Rack number
|
r
|
0
|
Virtual rack number.
|
|
Module position
|
m
|
0
|
Virtual module position
|
|
Channel
|
c
|
0 to 6
|
Input or output number
|
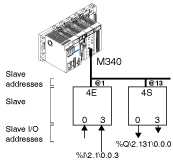
%I\2.1\0.0.3 indicates: input 3 of bus number 2 of slave TOR /A 1 and implicitly rack 0 and module 0 of the TSX SAY 1000 module.
%Q\2.131\0.0.0 indicates: output 0 of bus number 2 of slave TOR /B 131 and implicitly rack 0 and module 0 of the TSX SAY 1000 module.
%IW\2.38\0.0.0 indicates: input 0 of bus number 2 of slave ANA / A 38 and implicitly rack 0 and module 0 of the TSX SAY 1000 module.
Illustration:
NOTE: The physical address of an AS-i slave is programmed by a console.
An analog slave is configured only on slot /A.
The number of an extended TOR /B slave lies between 101 and 131.
The number of a standard TOR /A slave, or an ANA slave (which is always standard) lies between 1 and 31.
When a standard address setting slave is set at /A, an extended address setting slave at /B cannot have the same address. Only two extended address setting slaves can have the same address at /A and /B.
Multiple Address Settings
When one or more slaves are connected, make sure that you do not assign an address which is already being used by a slave on the bus.
If slave address is doubled then two scenarios may occur :