A VLAN is a group of Ethernet devices—which may be physically located on different network segments—that are grouped together and communicate as if they were located on the same LAN segment. All devices on a VLAN use the same IP subnet
In a port-based—or static—VLAN, an administrator configures VLAN membership by assigning individual switch ports to the VLAN. Any device connected to that port is effectively added to the VLAN.
NOTE: A single port can be a member of multiple VLANs.
VLANs permit the creation of logically separate groups of network devices, without having to physically re-wire those devices. When a switch receives a message directed to a specific VLAN, it forwards that message only to the switch ports that are members of that VLAN. The switch does not send the message to its ports that are not members of that VLAN.
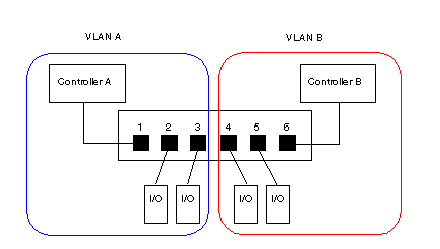
In the example, below, switch ports 1, 2, and 3 are assigned to VLAN A, while switch ports 4, 5, and 6 are assigned to VLAN B: